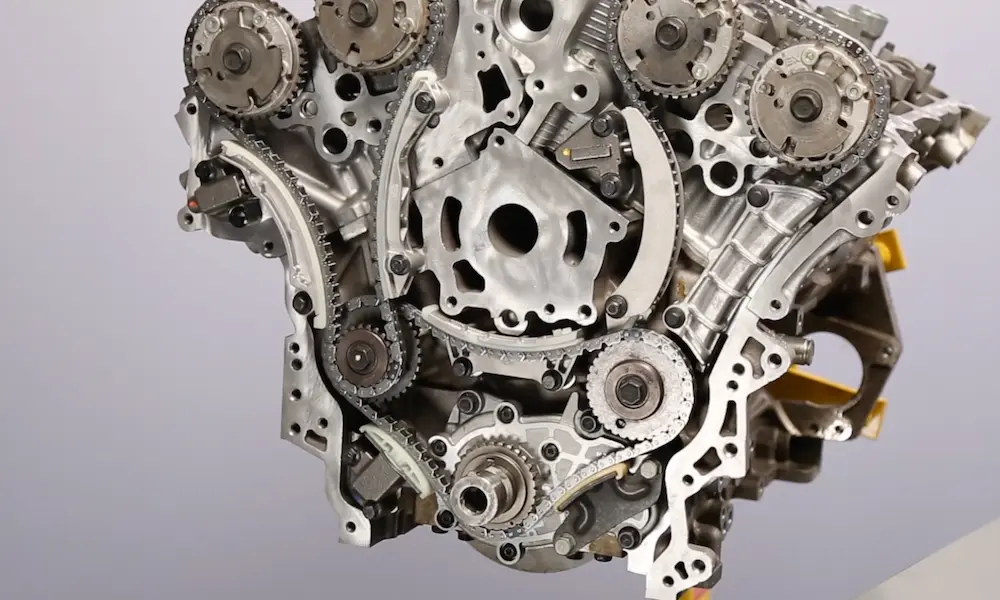
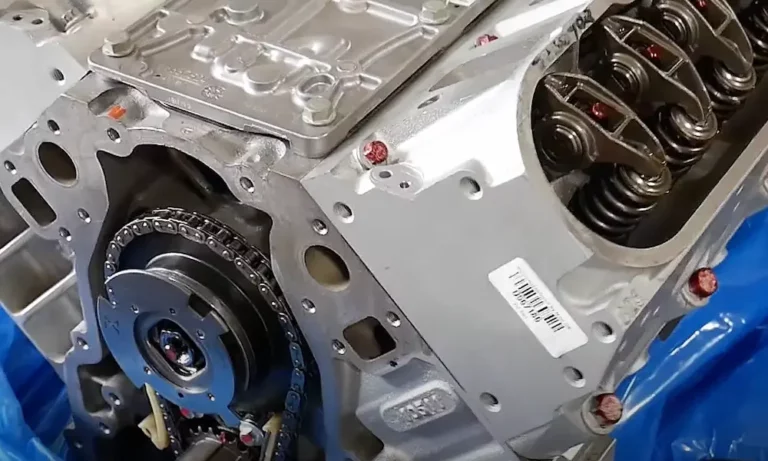
Ever wondered what makes Cadillac Escalades and GMC Yukons from the early 2010s move with such authority? It’s the heart of the beast—the L94 engine. This 6.2L powerhouse was GM’s premium offering for luxury SUVs, combining raw muscle with surprising sophistication.
What is the L94 Engine?
The L94 is a 6.2-liter V8 engine manufactured by General Motors from 2010 to 2014. Part of GM’s Generation IV Small Block family (also known as Vortec), this aluminum marvel delivered 403 horsepower and 417 lb-ft of torque—impressive numbers that made it the most powerful truck engine in GM’s lineup at the time.
Don’t confuse it with other GM V8s though. While it shares DNA with the Corvette’s LS3, the L94 was specifically engineered for truck and SUV applications, with a different torque curve and unique features.
L94 Engine History and Development
The L94 comes from automotive royalty. It’s a direct descendant of the legendary Chevrolet small-block V8 that revolutionized American engines back in 1955. By the time the L94 arrived, this engine family had evolved through four generations of improvements.
GM developed the L94 specifically for their premium SUVs, needing an engine that delivered both the power expected in high-end vehicles and the refinement demanded by luxury buyers.
Vehicles Equipped with the L94 Engine
The L94 wasn’t widely distributed across GM’s lineup. Instead, it was reserved for the cream of their SUV crop from 2010-2014:
- Cadillac Escalade (including ESV and EXT models)
- GMC Yukon Denali
- GMC Yukon XL Denali
If you’re checking a vehicle, look for the VIN code “F” in the 8th position—that’s the telltale sign of an L94 engine.
L94 vs. Related GM Engines
The L94 wasn’t an only child. It had two close siblings in GM’s engine family:
| Engine | Displacement | Active Fuel Management | Flex Fuel Capability | Typical Applications |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| L92 | 6.2L | No | No | 2007-2009 GM trucks/SUVs |
| L9H | 6.2L | No | Yes | 2007-2009 GM trucks/SUVs |
| L94 | 6.2L | Yes | Yes | 2010-2014 Luxury SUVs |
The L94 essentially took the L92 platform and added both Active Fuel Management and Flex Fuel capability, making it the most technologically advanced of the trio.
L94 Engine Performance Specifications
Let’s cut to the chase and look at what makes gearheads grin when discussing the L94.
Horsepower and Torque
The L94 wasn’t shy about showing its muscle:
- 403 horsepower at 5,700 RPM
- 417 lb-ft of torque at 4,300 RPM
These numbers put it at the top of GM’s truck engine lineup at the time. It’s worth noting that while the Corvette’s LS3 (a close relative) made more peak horsepower, the L94 was tuned for stronger low-end torque—exactly what you need when hauling a 5,500-pound luxury SUV.
Operating Specifications
- Compression ratio: 10.5:1
- Maximum engine speed: 6,000 RPM
- Fuel recommendation: Premium (but can run on regular with slightly reduced performance)
- Flex fuel compatible: Yes (can run on E85)
This high compression ratio helped squeeze out impressive power while the flex fuel capability gave owners options at the pump.
L94 Engine Block Specifications
The foundation of any engine is its block, and the L94’s was a testament to GM’s engineering prowess.
Block Design and Materials
Unlike many truck engines of the era that still used cast iron, the L94 featured an aluminum block that saved significant weight—crucial for improving the fuel economy of hefty luxury SUVs. Key details include:
- Material: Aluminum alloy
- Displacement: 6.2L (376 cubic inches)
- Block design: Deep-skirt for increased rigidity
- Main bearing caps: Six-bolt, cross-bolted design for strength
This wasn’t just any aluminum block—it benefited from GM’s extensive racing experience and was designed to handle substantial power while maintaining longevity.
Critical Dimensions
For the technically minded, here are the crucial measurements:
- Bore: 4.065 inches
- Stroke: 3.622 inches
- Deck height: 9.240 inches
- Bore spacing: 4.400 inches
- Main housing bore diameter: 2.751 inches
These precise dimensions reflect the careful engineering balance between power, efficiency, and durability.
L94 Rotating Assembly
The rotating assembly is where the magic happens in any engine, converting up-and-down motion into the rotational force that moves your vehicle.
Crankshaft and Connecting Rods
The L94 used:
- Cast iron crankshaft (GM part #12588613)
- Main journal diameter: 2.559 inches
- Rod journal diameter: 2.100 inches
- 58X reluctor wheel for precise ignition timing
- Powdered metal connecting rods with I-beam design
- Connecting rod length: 6.098 inches
These components were designed with both strength and durability in mind. The engine also featured a heavy-duty timing chain developed for quiet operation and validated for 200,000 miles of service.
Pistons and Compression Design
The pistons played a key role in achieving the L94’s 10.5:1 compression ratio:
- Material: Hypereutectic cast aluminum alloy
- Design: Flat top with valve reliefs
- Piston volume: +3cc
- Wrist pin: Full floating, 0.9431 inches diameter
This piston design offered an excellent balance between performance and longevity—important for a premium engine expected to deliver both power and reliability.
Cylinder Head and Valvetrain
The cylinder heads are where an engine breathes, and the L94’s lungs were designed for optimum airflow.
Cylinder Head Design
The L94 used aluminum cylinder heads with rectangle port design:
- Casting number: 823
- Material: Aluminum
- Combustion chamber volume: 68cc
- Intake port shape: Rectangle
- Intake runner volume: 257cc
- Exhaust port shape: D-port
- Exhaust runner volume: 87cc
While dimensionally similar to the LS3’s heads, the L94 heads had specific casting numbers and valve specifications optimized for truck applications, prioritizing low-end torque over high-RPM horsepower.
Valve Specifications
The valvetrain specifications reveal the engine’s breathing capabilities:
- Intake valve diameter: 2.165 inches
- Exhaust valve diameter: 1.590 inches
- Valve actuation: Hydraulic roller lifters
- Head bolt style: Torque-to-yield (TTY)
These relatively large valves helped the engine breathe effectively, contributing to its impressive power output.
Camshaft and Advanced Features
The camshaft is the brain of the engine, controlling when and how much the valves open. The L94’s cam was specifically designed for its intended applications.
Camshaft Specifications
The L94 camshaft (GM part #12623066) specifications:
- Intake duration @ .050″: 195 degrees
- Exhaust duration @ .050″: 201 degrees
- Intake valve lift: 0.500 inches
- Exhaust valve lift: 0.492 inches
- Lobe separation angle: 115 degrees
These specifications show a cam designed primarily for low-end and mid-range torque—perfect for moving heavy SUVs with authority.
Advanced Engine Technologies
What truly set the L94 apart were three key technologies:
1. Variable Valve Timing (VVT)
The L94 could adjust camshaft timing on the fly, providing:
- Flatter torque curve across the RPM range
- Higher peak horsepower
- Smoother idle quality
- Improved emissions
2. Active Fuel Management (AFM)
This cylinder deactivation system could shut down four cylinders during light load conditions, effectively turning the V8 into a V4 to save fuel. When more power was needed, all eight cylinders would fire up instantly.
3. Flex Fuel Capability
The L94 could run on E85 ethanol fuel (85% ethanol, 15% gasoline) or any blend down to regular gasoline, giving owners fueling flexibility while supporting alternative fuels.
Together, these technologies represented GM’s commitment to combining performance with efficiency in their premium engines.
Fuel and Ignition Systems
High performance requires precise fuel delivery and ignition timing.
Fuel System Components
The L94 used a sophisticated fuel system:
- Fuel delivery: Sequential multi-port fuel injection
- Injector type: High-flow with 4 nozzle holes (standard GM injectors had only 2)
- Operating pressure: 58 psi
- Fuel rail: High-flow aluminum design
The special 4-hole injectors were part of the Flex Fuel capability, allowing proper atomization regardless of the ethanol content in the fuel.
Ignition System Design
Reliable ignition was provided by:
- Coil-near-plug design (individual coil for each cylinder)
- Iridium-tipped spark plugs
- 58X crankshaft position sensor
- 4X camshaft position sensor
This design eliminated the distributor and spark plug wires, reducing maintenance needs while improving reliability and precision.
Cooling and Lubrication
Keeping a high-performance engine cool and well-lubricated is essential for longevity.
Cooling System
The L94’s cooling system was designed to maintain optimal operating temperatures even under heavy loads:
- Thermostat opening temperature: 180°F (82°C)
- Water pump: High-flow design
- Cooling capacity: 17.2 quarts with heavy-duty cooling package
The system was calibrated to warm up quickly for emissions control while preventing overheating during towing or high-load situations.
Oil System and Specifications
Proper lubrication was ensured by:
- Oil capacity: 8 quarts with filter
- Recommended oil: Dexos1 5W-30 synthetic blend
- Oil pressure (hot): 24 psi at 1000 RPM, 60 psi at 6000 RPM
- Oil pump: High-volume gerotor design
- Filter: AC Delco PF48 or equivalent
This robust lubrication system contributed to the engine’s durability and long service life.
Emissions and Environmental Features
The L94 was designed during a period of increasing emissions regulations, and GM incorporated several features to keep it compliant while maintaining performance.
Emissions Control Systems
Key emissions systems included:
- Three-way catalytic converters
- Air injection system
- Evaporative emissions control
- Positive crankcase ventilation (PCV)
- Exhaust gas recirculation (EGR)
These systems worked together to reduce harmful emissions without compromising the engine’s power delivery.
Fuel Economy Improvements
Several features specifically targeted improved fuel economy:
- Active Fuel Management (cylinder deactivation)
- Variable Valve Timing
- Aluminum block construction (weight reduction)
- Low-friction components
These technologies helped the L94-equipped vehicles achieve reasonable fuel economy for large, powerful SUVs of that era.
L94 Engine Reliability and Maintenance
No engine is perfect, and the L94 had its strengths and weaknesses from a reliability standpoint.
Common Issues and Solutions
While generally reliable, the L94 had a few known issues:
1. Active Fuel Management Problems
Some owners experienced issues with the AFM system, particularly lifter failures. A common solution was installing an AFM disabler to keep all cylinders active all the time.
2. Carbon Buildup
Direct injection engines of this era were prone to intake valve carbon buildup. Regular use of top-tier gasoline and occasional use of cleaning additives helped mitigate this.
3. Oil Consumption
Some engines developed slight oil consumption as they aged. Regular oil level checks and using the recommended synthetic blend oil helped manage this issue.
Maintenance Requirements
The L94 required typical maintenance for a modern V8:
- Oil changes: Every 5,000-7,500 miles with synthetic blend
- Spark plugs: 100,000 mile interval (iridium plugs)
- Air filter: 15,000-30,000 miles depending on conditions
- Coolant: 5-year/150,000-mile change interval (Dex-Cool)
Following these maintenance guidelines helped ensure the engine’s longevity and performance.
L94 Performance Potential and Modifications
As with most GM small-blocks, the L94 responds well to performance modifications.
Popular Upgrades
Common modifications that yield good results:
1. Intake and Exhaust Improvements
- Cold air intake: +10-15 HP
- Headers: +15-25 HP
- Cat-back exhaust: +5-10 HP
2. Engine Management
- ECU tuning: +20-30 HP and improved torque
- AFM delete: Improved reliability with minimal power gains
3. Forced Induction
- Supercharger kits: +150-200 HP
- Turbo systems: +150-300 HP depending on boost
Performance Benchmarks
Stock L94 engines typically produced:
- Quarter mile: 14.1-14.5 seconds (in Escalade/Yukon Denali)
- 0-60 mph: 6.5-7.0 seconds
With basic bolt-on modifications, these numbers could improve to:
- Quarter mile: 13.5-13.8 seconds
- 0-60 mph: 5.8-6.3 seconds
More extensive modifications with forced induction could yield:
- Quarter mile: 11.5-12.5 seconds
- 0-60 mph: 4.5-5.0 seconds
The L94’s Legacy and Replacement
The L94 represented the peak of GM’s Generation IV truck V8 development before being replaced by newer technologies.
Impact on Future GM Engines
The L94’s success influenced several aspects of future GM engines:
- Variable valve timing continued to be a core technology
- Cylinder deactivation evolved and improved
- Aluminum block construction became standard in most applications
The lessons learned from the L94 directly informed the development of the Generation V Small Block engines that followed.
Replacement: The EcoTec3 L86
In 2014, GM replaced the L94 with the 6.2L EcoTec3 L86 engine, which featured:
- Direct fuel injection (versus port injection)
- Improved Active Fuel Management
- More sophisticated variable valve timing
- Higher compression ratio (11.5:1)
- Increased power: 420 HP and 460 lb-ft of torque
The L86 built upon the L94’s foundation while incorporating new technologies to improve both power and efficiency.
L94 Engine for Enthusiasts Today
Even though production ended in 2014, the L94 remains significant to enthusiasts and those maintaining these vehicles.
Finding and Identifying an L94
If you’re looking at a used vehicle or engine:
- Check the 8th digit of the VIN for code “F”
- Look for the engine code on the front of the block
- Count the injector nozzle holes: 4 holes indicate an L94 flex-fuel injector
- Check for AFM components like the special lifters and valley cover
Current Market Values
As of 2023, market values for L94 engines vary:
- Complete used engines: $3,500-$6,000 depending on mileage and condition
- Remanufactured engines: $7,000-$9,000
- Core values: $300-$500
These engines remain popular for swaps into older GM vehicles due to their power, electronic controls, and relative simplicity compared to newer direct-injection engines.
L94 Technical Specifications Table
For easy reference, here’s a comprehensive specifications table for the L94 engine:
| Specification | Details |
|---|---|
| Engine Type | 90° V8, Generation IV Small Block |
| Displacement | 6.2L / 376 cubic inches |
| Bore × Stroke | 4.065 × 3.622 inches |
| Compression Ratio | 10.5:1 |
| Horsepower | 403 HP @ 5,700 RPM |
| Torque | 417 lb-ft @ 4,300 RPM |
| Block Material | Aluminum |
| Cylinder Head Material | Aluminum |
| Valvetrain | Overhead valve, 2 valves per cylinder |
| Valve Sizes | Intake: 2.165″, Exhaust: 1.590″ |
| Fuel System | Sequential multi-port fuel injection |
| Fuel Compatibility | Regular gasoline, premium recommended, E85 compatible |
| Advanced Features | Variable valve timing, Active Fuel Management, Flex Fuel |
| Oil Capacity | 8 quarts with filter |
| Production Years | 2010-2014 |
The L94 represents an important chapter in GM’s engine development story—combining muscle car power with truck durability and surprising efficiency. Whether you’re maintaining one in your luxury SUV or considering it for an engine swap project, the L94 remains a powerful and capable option even years after its production ended.