Thinking about the legendary 6.4 Powerstroke? This workhorse diesel engine powered Ford Super Duty trucks from 2008 to 2010, marking an important chapter in Ford’s diesel timeline. While it had a relatively short production run, this engine packed innovative features and serious power that still makes it relevant today.
Let’s dive into everything about the 6.4 Powerstroke – from its basic specs and unique design features to performance capabilities and common issues. Whether you’re considering buying a used truck with this engine or just appreciate diesel engineering, you’ll find all the essential details here.
6.4 Powerstroke Basic Specifications
The 6.4 Powerstroke represents the third generation of Power Stroke engines and the final collaboration between Ford and International-Navistar. Here are the fundamental specs:
- Production years: 2008-2010
- Configuration: V8 diesel
- Displacement: 6,369cc (388.7 cubic inches)
- Bore: 3.87 inches (98.3mm)
- Stroke: 4.13 inches (104.9mm)
- Compression ratio: 17.0:1
- Horsepower: 350 hp @ 3,000 rpm
- Torque: 650 lb-ft @ 2,000 rpm
- Idle speed: Approximately 650 rpm
- Governed speed: Approximately 3,000 rpm
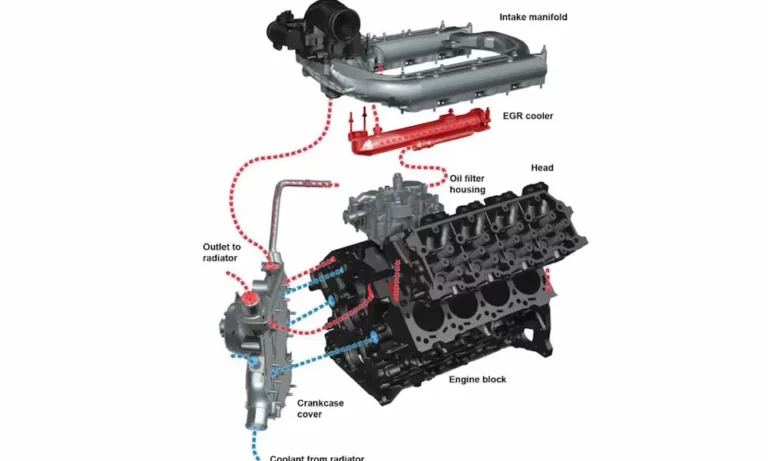
The engine featured cast-iron block and heads, providing the durability needed for heavy-duty applications. One standout design element was the cast iron bed plate that replaced traditional main bearing caps, secured with four bolts per main bearing. This significantly improved bottom-end strength and crankshaft stability under load.
Revolutionary Twin-Turbo System
The 6.4 Powerstroke made history as the first factory-installed twin-turbocharger system in its segment. This innovative setup gave it a significant performance advantage over competitors and previous models.
How the Sequential Turbos Work
The compound turbocharger system combined two different turbochargers working in sequence:
- A 65mm fixed geometry low-pressure turbocharger
- A 52mm variable geometry high-pressure turbocharger
In operation, air first entered the larger, low-pressure turbo before being directed to the smaller, high-pressure turbo, and finally into the engine through an air-to-air intercooler. This sequential design dramatically reduced turbo lag while providing more consistent power delivery across the RPM range.
The result? A diesel engine that felt more responsive and linear in its power delivery, almost like a naturally aspirated engine, but with all the torque advantages of forced induction.
Advanced Fuel Injection Technology
The 6.4 Powerstroke marked a significant departure from previous Power Stroke engines by abandoning the Hydraulic Electronic Unit Injector (HEUI) system in favor of more sophisticated technology.
Common Rail System
This engine utilized a high-pressure common rail direct injection system built around a Siemens VDO K16 high-pressure fuel pump located at the rear of the lift valley. The system could produce fuel pressures up to 24,650 psi – an impressive figure that enabled precise fuel atomization and better combustion control.
Piezoelectric Injectors
Perhaps the most advanced feature was the piezoelectric injectors. These sophisticated components could execute up to five separate injection events during each cylinder’s power stroke. This technology was revolutionary compared to earlier Power Stroke engines and contributed to:
- Better performance across the RPM range
- Reduced emissions and particulate matter
- Improved combustion efficiency
- Smoother, quieter operation
This precision injection capability was a game-changer that influenced diesel engine development for years to come.
Real-World Performance Numbers
On paper, the 6.4 Powerstroke’s 350 horsepower and 650 lb-ft of torque were impressive for the time. But what did this mean for real-world capability?
Towing and Hauling Capacity
When properly equipped, Ford Super Duty trucks with the 6.4 Powerstroke could handle:
- Conventional towing: Up to 16,000 pounds
- Fifth-wheel towing: Up to 24,600 pounds
- Payload capacity: Up to 6,180 pounds
These numbers made the trucks exceptionally capable workhorses for commercial applications, heavy towing, and recreational use.
Performance Potential
The 6.4 Powerstroke gained a reputation for its substantial performance upgrade potential. The powdered-metal connecting rods were significantly stronger than those in the 6.0L Powerstroke and capable of handling more than 900 rear-wheel horsepower in modified applications.
This made the engine popular among performance enthusiasts looking for a strong foundation for modifications. With relatively simple upgrades like tuning, exhaust modifications, and cold air intakes, owners could easily boost output by 100+ horsepower and 200+ lb-ft of torque.
Emissions Control Systems
As emissions regulations tightened, the 6.4 Powerstroke introduced several new technologies to reduce its environmental impact.
Diesel Particulate Filter
The 6.4L was the first Power Stroke engine to utilize a Diesel Particulate Filter (DPF), which significantly reduced particulate emissions by trapping soot and other particles from the exhaust. This system virtually eliminated the black smoke typically associated with diesel engines during acceleration.
The DPF employed a regeneration process where the engine computer periodically injected extra fuel during the exhaust stroke to burn off accumulated soot within the filter. While effective at maintaining emissions compliance, this regeneration process introduced some complexity and maintenance considerations that owners should understand.
Overall Emissions Reductions
Compared to the 6.0L Power Stroke, the 6.4L achieved impressive emissions reductions:
- NOx (nitrogen oxides) reduced by 50%
- Particulate matter reduced by 90%
These reductions were achieved while simultaneously increasing horsepower and torque – representing a significant engineering achievement for the time.
Reliability Enhancements
Learning from experiences with the 6.0L Power Stroke, Ford and International implemented several design improvements to enhance the reliability of the 6.4L engine.
Head Gasket and Bolt Improvements
One notable upgrade was the use of larger 16mm cylinder head bolts instead of the 14mm bolts used in the 6.0L engine. This increased the clamping force on the head gaskets, addressing one of the common failure points in the previous engine generation.
Connecting Rod Strength
The 6.4L utilized powdered-metal connecting rods significantly stronger than those in the 6.0L Power Stroke. These robust connecting rods contributed to the engine’s ability to handle higher power levels and provided better durability under stress.
Common Issues and Maintenance Considerations
While the 6.4 Powerstroke offered impressive performance, it wasn’t without its challenges. Being aware of these can help owners maintain their engines properly.
Emissions System Complications
The DPF system, while effective at controlling emissions, created several potential issues:
- Reduced fuel economy during regeneration cycles
- Potential for clogging if regeneration cycles were interrupted
- Additional complexity that could lead to costly repairs
Many owners chose to remove these systems through aftermarket modifications, though this practice raises both legal and environmental concerns.
Radiator and Cooling Issues
The cooling system on 6.4 Powerstroke trucks was sometimes inadequate for heavy towing in hot climates. Upgrading to higher-capacity radiators and improved cooling fans became a common modification for owners who frequently towed heavy loads.
Fuel Dilution in Oil
The 6.4’s regeneration system could sometimes lead to fuel dilution in the engine oil, especially during frequent short trips that didn’t allow the engine to reach full operating temperature. Regular oil analysis and adherence to maintenance schedules became particularly important for these engines.
Maintenance Schedule and Recommendations
Proper maintenance is crucial for maximizing the longevity of a 6.4 Powerstroke. Here’s what owners should keep in mind:
- Oil changes: Every 5,000 miles with high-quality 15W-40 or 10W-30 diesel-specific oil
- Fuel filters: Replace both primary and secondary filters every 10,000 miles
- Air filters: Inspect every 5,000 miles, replace as needed
- Coolant: Change every 60,000 miles with the correct Ford-specified coolant
- Transmission fluid: Change every 30,000 miles for severe duty or towing applications
Following these maintenance guidelines can help prevent many of the common issues associated with these engines.
How the 6.4 Compares to Other Power Stroke Engines
The 6.4 Powerstroke holds a unique position in Ford’s diesel engine lineage.
6.4L vs. 6.0L Powerstroke
Compared to its predecessor:
- More power and torque (350hp/650lb-ft vs. 325hp/570lb-ft)
- More reliable head gasket design with larger head bolts
- Twin-turbo system vs. single variable geometry turbo
- Common rail injection vs. HEUI system
- Better emissions control but more complex systems
6.4L vs. 6.7L Powerstroke
Compared to its successor:
- Lower factory power ratings (6.7L started at 390hp/735lb-ft)
- Less sophisticated emissions controls
- International design vs. Ford in-house design
- Typically considered less fuel-efficient
- Often praised for its simpler overall design despite emissions complexity
Buying a Used Truck with a 6.4 Powerstroke
If you’re considering purchasing a used truck with this engine, here are some essential tips:
What to Look For
- Service records: Comprehensive maintenance history is crucial
- Emissions system status: Has it been modified or deleted? This affects both legality and value
- Engine oil analysis: Can reveal internal wear or fuel dilution issues
- Coolant condition: Should be clear with no oil contamination
- Turbo performance: Listen for unusual sounds during acceleration or deceleration
- EGR system: Often problematic, should be properly functioning or upgraded
Questions to Ask the Seller
- Has the truck had any major engine repairs?
- Are both turbos original or have they been replaced?
- Has the emissions system been modified?
- What type of driving was the truck used for? (Towing, highway, city)
- What maintenance schedule was followed?
Upgrade Paths for 6.4 Powerstroke Owners
For those looking to improve their 6.4 Powerstroke, several upgrade paths exist:
Performance Upgrades
- Tuning: Custom ECM tuning can add significant power
- Cold air intake: Improves airflow and can add 10-20 horsepower
- Exhaust system: 4-inch turbo-back exhaust systems reduce backpressure
- Upgraded intercooler: Reduces intake temperatures for more power and engine protection
- Stronger turbo components: For those seeking significant power increases
Reliability Upgrades
- Oil cooler: Upgraded units help maintain proper oil temperatures
- EGR solution: EGR cooler upgrades or bypass systems (where legal)
- Fuel filtration: Additional or upgraded fuel filters protect injectors
- Coolant filtration: Helps prevent cooling system issues
The Legacy of the 6.4 Powerstroke
Despite its short production run, the 6.4 Powerstroke made a lasting impact on diesel engine development. As the final collaboration between Ford and International-Navistar, it represented both the culmination of their joint efforts and a transitional technology that influenced future designs.
The twin-turbo system pioneered in this engine would influence many future diesel designs, while its common rail injection system and piezoelectric injectors set new standards for precision in diesel fuel delivery.
Though replaced by the 6.7L Power Stroke in 2011, the 6.4L remains popular among enthusiasts who appreciate its robust design and modification potential. With proper maintenance and thoughtful upgrades, these engines can continue to deliver impressive performance and reliability for years to come.