You’re cruising down the highway in your Chevy Volt when suddenly, a warning flashes on your dashboard: “Propulsion Power is Reduced.” The car feels sluggish, and you’re no longer able to maintain highway speeds. What’s happening? Is it safe to continue driving? And how can you fix it?
This comprehensive guide dives into everything you need to know about this common Chevy Volt warning, from what causes it to how you can resolve it.
What Does “Propulsion Power is Reduced” Mean on a Chevy Volt?
When your Chevy Volt displays the “Propulsion Power is Reduced” message, it’s telling you that your vehicle can’t deliver its normal power output. This warning appears specifically when the battery reports less than 35kW of power available for any reason.
In practical terms, this means:
- Your acceleration will be noticeably slower
- The engine will likely run at consistently higher power than normal
- You may struggle to maintain highway speeds (some owners report being unable to drive faster than 35 mph)
- Your electric range may be significantly decreased
This isn’t just an inconvenience—it’s a safety issue. When your Volt enters reduced power mode, you’re using reserve power, which can be extremely dangerous for your hybrid battery if continued for extended periods. In severe cases, the power reduction happens with little to no warning, creating potentially hazardous situations, especially in high-traffic areas or when merging onto highways.
When Does This Warning Typically Appear?
Your Chevy Volt might display this warning in several scenarios:
- When driving in mountainous terrain without using Mountain Mode
- During aggressive driving when the battery reserve has been depleted
- Upon startup in extremely cold temperatures (below -15°C/5°F), especially if the vehicle has been left unplugged
- When there’s a malfunction in the Battery Energy Control Module (BECM)
- If there are problems with the high-voltage battery pack
- When electrical system faults occur
The message is often accompanied by the Malfunction Indicator Light (check engine light) and potentially by diagnostic trouble code P0A7F.
Common Causes of Reduced Propulsion Power in Chevy Volts
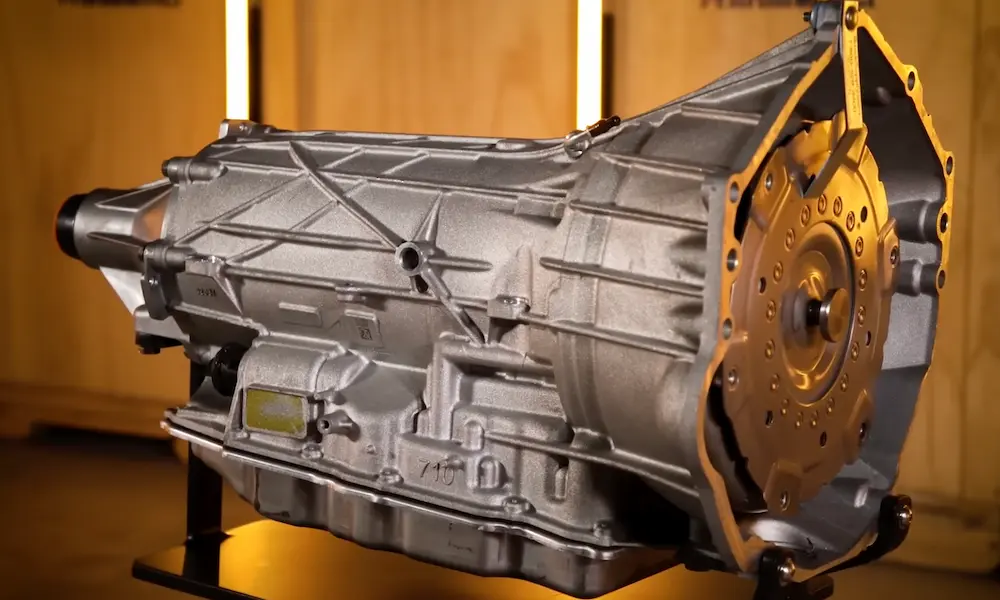
1. Battery Pack Performance Issues
The high-voltage battery pack is the heart of your Volt’s propulsion system. When cells in this battery malfunction, it significantly decreases available power. Battery degradation is a natural process as vehicles age, but premature or severe degradation can trigger the propulsion power reduced message.
Over time, your Volt’s battery may lose capacity, reducing both your electric range and the power available to the propulsion system. This degradation accelerates if the battery is frequently deeply discharged or exposed to extreme temperatures.
2. Battery Energy Control Module (BECM) Failures
The BECM is a critical component that manages energy flow between the battery pack and vehicle systems. When it malfunctions, your Volt may experience:
- Reduced propulsion power
- Failure to start
- Inability to charge when plugged in
This issue has become so widespread that GM issued a Special Coverage bulletin in March 2024 extending the warranty for this specific component on 2016-2018 Chevy Volt PHEVs to 15 years or 150,000 miles.
3. Electrical System Problems
The Volt’s sophisticated hybrid system relies on proper electrical connections and components. Faults in the electrical system—including problems with the AC/DC converters or power distribution components—can trigger the propulsion power reduced warning.
Sometimes these issues are related to the 12V auxiliary battery, which powers many of the vehicle’s systems even though it’s not directly involved in propulsion.
4. Exhaust Gas Recirculation (EGR) Issues
When the check engine light accompanies your propulsion power reduced warning, it may indicate EGR problems. In some cases, the F03 fuse in the engine compartment fuse box might be blown. While replacing this fuse isn’t a permanent solution, it might allow you to drive several miles before the issue returns.
5. Environmental and Driving Factors
Your driving habits and environmental conditions can also trigger this warning:
- Driving in mountainous terrain without activating Mountain Mode
- Aggressive acceleration that rapidly depletes the battery
- Operating in extremely cold temperatures, especially if the car hasn’t been plugged in
- Continuous high-speed driving that depletes the battery faster than expected
Official GM Recalls and Service Bulletins for This Issue
General Motors has issued several service bulletins and customer satisfaction programs related to the propulsion power reduced issue:
Customer Satisfaction Program 17228
This program specifically addressed reduced propulsion power in 2017 model year Chevrolet Volt vehicles with automatic transmission (RPO MKV). The remedy was reprogramming the hybrid powertrain control module 2, offered at no charge until June 30, 2019.
Special Coverage for BECM Malfunction (N232432680)
In March 2024, GM extended warranty coverage for the battery energy control module in 2016-2018 Chevy Volt PHEVs to 15 years or 150,000 miles. This covers:
- BECM replacement
- Adding up to 8 quarts of coolant
- About 5 hours of labor
NHTSA Investigation
In December 2023, the National Highway Traffic Safety Administration opened a preliminary investigation into approximately 73,000 Chevrolet Volt plug-in hybrid cars from model years 2016-2019. The investigation focuses on reports of abrupt power loss, failure to restart, and other BECM-related issues that could pose safety risks.
What to Do When You See This Warning
Immediate Actions When the Warning Appears
- Slow down and pull over as soon as it’s safe to do so
- Assess whether it’s safe to continue driving at reduced power
- If the warning appears alongside the check engine light, it’s advisable to have your vehicle serviced by a dealer rather than continuing to drive
- If you must continue driving, minimize acceleration demands and maintain a steady speed
Preventive Measures: Using Mountain Mode
The Volt’s Mountain Mode was specifically designed to reserve battery power for climbing steep grades. To use it effectively:
- Press the Drive Mode button three times after unplugging your Volt
- Or activate it about 20-25 minutes before you start climbing a grade
- This reserves some battery charge to use during the climb, helping to prevent the propulsion power reduced warning
Even with Mountain Mode activated, the warning might still appear during exceptionally steep climbs, but this is considered normal operation in extreme conditions.
Comparing Propulsion Power Issues Across Chevy Volt Model Years
| Model Year | Common Propulsion Power Issues | Applicable Service Programs | Notable Features |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2016-2018 | BECM failures, battery degradation | Special Coverage N232432680 | 15yr/150,000 mile BECM warranty |
| 2017 | Propulsion power reduced with DTC P0A7F | Customer Satisfaction Program 17228 | Hybrid powertrain control module reprogramming |
| 2019 | Included in NHTSA investigation | None specific to this model year | Generally more reliable battery system |
Long-Term Considerations for Volt Owners
Parts Availability Challenges
Some Chevy Volt owners have reported waiting months for replacement battery modules. While GM claims to have sufficient replacement parts in its supply pipeline, extended waiting periods for these components can leave owners without a functioning vehicle for prolonged periods.
Battery Health Management
To maintain your Volt’s battery health and minimize the risk of propulsion power issues:
- Avoid letting the battery sit completely charged or completely discharged for extended periods
- When possible, keep the vehicle plugged in during extreme temperatures
- Use mountain mode preemptively when facing challenging driving conditions
- Follow the manufacturer’s recommended maintenance schedule
- Have the cooling system checked regularly, as proper battery temperature management is critical
Understanding the Technical Side of Propulsion Power Reduction
The Chevy Volt’s propulsion system is a complex integration of electric motors, a high-voltage battery pack, and a gasoline engine. When the system detects a potential issue that might damage components or create unsafe conditions, it enters a protective “limp home” mode—what you see as propulsion power reduced.
This protective measure can be triggered by:
- Battery cells operating outside their safe temperature range
- Voltage imbalances between battery modules
- Current sensors detecting abnormal power flows
- Communication errors between control modules
- Physical damage to high-voltage components
The system prioritizes safety over performance, which is why your Volt will always err on the side of reducing power rather than risking damage to expensive components or potential safety hazards.
Solving Propulsion Power Reduced Issues
DIY Approaches (For Minor Cases)
For temporary or minor propulsion power reduced warnings:
- Reset the system: Fully power off the vehicle, wait 10 minutes, then restart. This sometimes clears temporary electronic glitches.
- Check for updates: Verify if your vehicle’s software is up to date. Some issues have been addressed through programming updates.
- Use Mountain Mode strategically: If you know you’ll be driving in challenging conditions, activate Mountain Mode in advance to maintain adequate power reserves.
- Monitor battery temperature: In extremely cold weather, keep your Volt plugged in when not in use to maintain optimal battery temperature.
Professional Repairs for Persistent Issues
For recurring or severe propulsion power reduced warnings:
- BECM replacement: If your Battery Energy Control Module is failing, it will need professional replacement. This repair takes about 5 hours and is covered under the extended warranty for eligible vehicles.
- Battery pack service: Individual modules or the entire high-voltage battery may need to be replaced if cells are degraded or damaged.
- Electrical system diagnosis: A professional can trace and repair faults in the complex electrical systems that might be triggering the warning.
- Control module reprogramming: Updated software might resolve issues with how the vehicle’s computers manage power distribution.
When seeking professional help, choose a service center familiar with hybrid vehicles. Not all mechanics have the specialized training and equipment needed to diagnose and repair high-voltage hybrid systems safely.
When to Consider Trading In Your Chevy Volt
If you’re experiencing constant propulsion power reduced warnings despite repairs, you might consider:
- Trading for a newer model with improved reliability
- Switching to a different hybrid or electric vehicle brand
- Exploring GM’s buyback options if your vehicle qualifies as a lemon under your state’s laws
Before making this decision, document all repair attempts, save service records, and research the specific laws in your state regarding vehicle warranties and lemon laws.
Remember that the Chevy Volt, despite these issues, was a pioneering vehicle that helped advance hybrid technology. Most owners report many years of reliable service when proper maintenance is followed.