Ever wondered what makes a Hellcat roar? It’s not just the badge—it’s the engineering marvel hiding under the hood. Dodge’s Hellcat engine has become legendary among muscle car enthusiasts, redefining what’s possible in modern American performance.
If you’re considering a Hellcat-powered vehicle or just fascinated by automotive engineering, you’ll want to understand exactly what makes this powerplant so special. Let’s dive into the specs that create all that tire-shredding power.
What Makes a Hellcat a Hellcat?
The Hellcat engine is Dodge’s supercharged 6.2-liter HEMI V8—but that simple description doesn’t do it justice. This powerplant represents the peak of traditional American muscle car philosophy combined with modern engineering.
Developed after the 2008 recession when Fiat took over Chrysler, the Hellcat engine merged Italian racing expertise with American muscle traditions. The result? A completely reimagined engine that shares only basic architecture with other HEMI V8s.
Unlike many high-performance engines that sacrifice reliability for power, the Hellcat was designed to deliver both. You can drive it daily and still unleash supercar-level performance when you want.
Core Performance Specs: The Numbers That Matter
Let’s talk raw numbers. In standard form, the Hellcat engine produces:
- 707-717 horsepower (depending on model year)
- 645-656 lb-ft of torque
- 9.5:1 compression ratio
- 14.5 psi of boost pressure (standard version)
This powerplant launched in the 2015 Dodge Challenger SRT Hellcat before expanding to other vehicles. Over time, Dodge created even more powerful variants:
| Hellcat Version | Horsepower | Torque (lb-ft) | Notable Features |
|---|---|---|---|
| Standard Hellcat | 707-717 | 645-656 | 2.7L supercharger, 14.5 psi boost |
| Hellcat Redeye | 797 | 707 | Larger supercharger, increased boost |
| Widebody Jailbreak | 807 | 707 | Enhanced cooling, revised calibration |
| Challenger SRT Demon | 840 | 770 | Race fuel compatible, drag-specific tuning |
The engine has powered multiple vehicles in the Dodge/Jeep lineup, including the Challenger, Charger, Durango, Ram TRX, and Jeep Grand Cherokee Trackhawk.
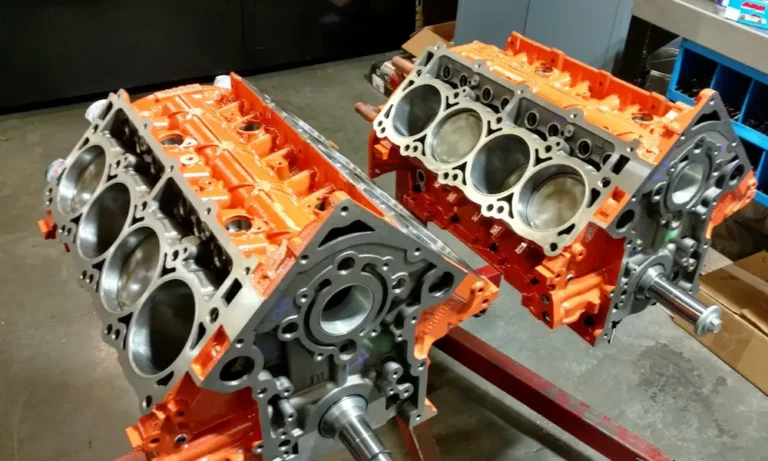
The Engine Block: Built for Strength
The foundation of the Hellcat’s impressive performance starts with its block. Unlike many modern engines that use aluminum to save weight, the Hellcat uses an iron block for maximum strength.
Key block specifications include:
- Cast iron construction (casting number 5037473BE)
- 6.2 liters (376 cubic inches) displacement
- 4.090-inch bore diameter
- 3.580-inch stroke
- 9.280-inch deck height
- 4.460-inch bore spacing
The block features five main bearings with an innovative design: each main cap uses two primary bolts plus two cross-bolts for exceptional rigidity. This prevents crankshaft flex under extreme power, a critical feature when you’re pushing over 700 horsepower.
Rotating Assembly: Handling Massive Forces
Inside that robust block lives a rotating assembly built to handle enormous stress. Key components include:
- Forged steel crankshaft (part number 68495868AA)
- 2.559-inch main journal diameters
- 2.126-inch rod journal diameters
- Forged pistons with dish-top design
- Powdered metal connecting rods with I-beam design
- 6.200-inch rod length
- 0.9451-inch wrist pin diameter
This assembly is designed to withstand the substantial forces generated when you unleash full power. The forged components provide greater strength than cast parts, reducing the risk of catastrophic failure when the engine is pushed to its limits.
Cylinder Head and Valvetrain: Breathing Fire
The Hellcat’s cylinder heads are engineering masterpieces that enable its impressive power output. Made from aluminum to reduce weight, these heads feature:
- 74cc combustion chambers
- Square intake ports (202.5cc volume)
- D-shaped exhaust ports (68cc volume)
- Large valves (2.138-inch intake, 1.654-inch exhaust)
- Hollow stem intake valves
- Sodium-filled hollow stem exhaust valves for better cooling
- 18° intake valve angle and 16.5° exhaust valve angle
The camshaft specs reveal how the engine manages airflow:
- 221° intake duration (at 0.050-inch lift)
- 225° exhaust duration (at 0.050-inch lift)
- 0.571-inch maximum intake valve lift
- 0.536-inch maximum exhaust valve lift
- 120° lobe separation angle
- Variable cam timing capability
Unlike some other HEMI engines, the Hellcat doesn’t use the Multiple Displacement System (MDS) that deactivates cylinders for fuel economy. This is a pure performance engine with no compromises.
Supercharger System: Force-Feeding the Beast
The heart of the Hellcat’s power is its supercharger system. Rather than using turbochargers that rely on exhaust gases, the Hellcat employs a twin-screw supercharger that delivers immediate throttle response.
Key supercharger specifications include:
- 2.7-liter twin-screw design (standard Hellcat)
- 14.5 psi of boost pressure
- 92mm electronic throttle body
- High-flow fuel injectors (42 lbs/hr at 58 psi)
- Dedicated charge air cooling system
The supercharger is belt-driven directly from the crankshaft, which means it responds instantly to throttle inputs without the lag associated with turbochargers. This creates the immediate, visceral power delivery that Hellcat engines are famous for.
Fuel System: Feeding the Fire
To support 700+ horsepower, the Hellcat needs a robust fuel system. The engine uses:
- High-flow fuel injectors (part number 68170238AB)
- 42 pounds per hour flow rate at 58 psi
- 1.900-inch length between O-rings
- USCAR/EV6 connector design
The standard Hellcat engine is not flex-fuel capable, meaning it’s designed for premium gasoline rather than ethanol blends. The Demon variant, however, was designed to run on racing fuel for maximum output.
These fuel system components work with the GPEC2A powertrain control module to precisely meter fuel delivery across the entire operating range.
Hellcat Engine Applications: Where You’ll Find Them
Since its introduction, the Hellcat engine has powered a growing family of high-performance vehicles:
- Dodge Challenger SRT Hellcat (2015-2023)
- Dodge Charger SRT Hellcat (2015-2023)
- Jeep Grand Cherokee Trackhawk (2018-2021)
- Dodge Durango SRT Hellcat (2021-present)
- Ram 1500 TRX (2021-2022)
Each application features specific calibrations to match the vehicle’s character. The Challenger variants received the most powerful versions, while the SUVs and trucks were tuned for slightly different power delivery to match their weight and intended use.
Hellcat Variants: From Powerful to Ridiculous
The standard Hellcat was just the beginning. Dodge pushed the platform even further with several variants:
Hellcat Redeye
With 797 horsepower, the Redeye took the standard Hellcat formula and amplified it. Changes included:
- Increased boost pressure
- Enhanced cooling system
- Revised calibration
- Strengthened internal components
Widebody Jailbreak
The Jailbreak package pushed output to 807 horsepower, making it the most powerful non-Demon Hellcat. For the 2023 model year, Dodge made this package available on both Redeye and non-Redeye models.
Challenger SRT Demon
The ultimate factory Hellcat, the limited-production Demon was built specifically for drag racing with:
- 840 horsepower on 100+ octane racing fuel (808 hp on premium pump gas)
- 770 lb-ft of torque
- 2.4-liter supercharger (smaller but with different tuning)
- 11.6 psi boost level (optimized differently than standard Hellcat)
- Drag-specific suspension and transmission tuning
- Factory trans-brake for launch control
The Demon could run the quarter-mile in 9.65 seconds—quick enough that the NHRA actually banned it from competition without additional safety equipment.
Lubrication and Cooling: Keeping It All Together
With great power comes great heat, and managing that heat is critical to the Hellcat’s reliability. The engine employs:
- Gerotor-type oil pump (part number 68195993AD)
- Application-specific oil pans (front sump for cars, rear sump for trucks/SUVs)
- High-performance cooling system with dedicated heat exchangers for the supercharger
- 0W-40 synthetic oil recommendation
These systems work together to keep operating temperatures in check, even during extended high-performance driving.
The End of an Era
The 2023 model year marks the end of the current generation Hellcat-powered vehicles. All 2023 models receive special “Last Call” plaques commemorating the end of this chapter in American performance history.
As Dodge transitions toward electrified performance, the Hellcat engine stands as perhaps the ultimate expression of traditional American muscle—a fitting finale to the supercharged V8 era.
Comparing Hellcat to Other Performance Engines
How does the Hellcat stack up against other high-performance engines? Here’s a quick comparison:
| Engine | Displacement | Power | Forced Induction | Notable Feature |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hellcat 6.2L | 6.2L (376ci) | 707-840hp | Supercharged | Highest hp-per-dollar ratio |
| Dodge 6.4L Scat Pack | 6.4L (392ci) | 485hp | Naturally aspirated | Modern take on classic 392 HEMI |
| Ford 5.2L Predator | 5.2L (317ci) | 760hp | Supercharged | Powers Mustang GT500 |
| GM LT4 | 6.2L (376ci) | 650-668hp | Supercharged | Used in Corvette Z06, Camaro ZL1 |
What makes the Hellcat stand out is its combination of raw power and relative accessibility. While still expensive, Hellcat-powered vehicles deliver supercar performance at a fraction of exotic car prices.
Maintaining a Hellcat Engine
Owning a Hellcat means having responsibilities. These engines require proper care:
- Premium fuel only (91+ octane, 100+ for Demon at full power)
- Regular oil changes with manufacturer-recommended synthetic oil
- Periodic supercharger oil changes
- Attention to cooling system condition
- Quality filters for both air and oil
The good news is that despite their performance potential, Hellcat engines have proven remarkably reliable when properly maintained. Many owners report trouble-free operation even with moderate modifications for additional power.
Aftermarket Potential: Making a Monster Even Stronger
The Hellcat’s overbuilt nature makes it an excellent platform for aftermarket modifications. Common upgrades include:
- Smaller supercharger pulleys for increased boost
- Cold air intake systems
- Custom ECU tuning
- Header and exhaust upgrades
- E85 ethanol conversion
With relatively modest modifications, Hellcat engines can produce over 900 horsepower while maintaining reasonable reliability. More extreme builds have exceeded 1,000 horsepower with internal engine modifications.
The Legacy of the Hellcat Engine
As we approach the end of the Hellcat era, it’s worth considering this engine’s place in automotive history. The Hellcat will likely be remembered as one of the last and greatest examples of traditional American V8 muscle—a spectacular final chapter before the industry transitions to electrification.
What makes the Hellcat special isn’t just its impressive numbers but how it delivers its performance. The immediate throttle response, the distinctive supercharger whine, and the raw, unfiltered character create an experience that electric vehicles, despite their performance capabilities, simply can’t replicate.
The Hellcat engine proved that American performance engineering could compete with the world’s best while maintaining its unique character. That’s a legacy worth celebrating.