Ever looked under your car and wondered exactly which GM transmission you’re dealing with? You’re staring at that metal box with no idea whether it’s a Powerglide, TH350, or something more modern like the 8L90E. Identifying your GM transmission doesn’t have to be a guessing game. With the right approach, you can pinpoint exactly what you’re working with—saving time, money, and frustration before your next repair or upgrade.
How to Identify Any GM Transmission
GM has produced hundreds of transmission models over the decades. Fortunately, there are several reliable ways to figure out exactly what you’re looking at.
Look at the Pan Shape First
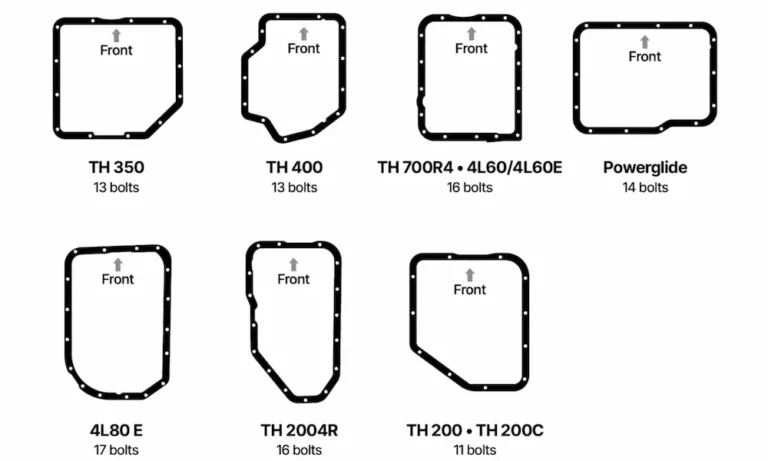
The easiest way to identify most GM automatic transmissions is by examining the shape of the transmission pan and counting the bolts. Each transmission family has a distinctive pan configuration that serves as an immediate visual identifier.
Here’s what to look for:
| Transmission | Bolt Count | Pan Shape Description |
|---|---|---|
| Powerglide | 14 | Sideways rectangular shape |
| TH350 | 13 | Square with corner notches |
| TH400 | 13 | Irregular “Texas-shaped” outline |
| TH200/TH200C | 11 | Small rectangular with “METRIC” stamp |
| TH200-4R | 16 | Rectangular configuration |
| 700R4/4L60/4L60E | 16 | Rectangular with rounded corners |
| 4L80E | 17 | Very large rectangular pan |
For example, if you spot a pan with 13 bolts in a Texas-like shape, you’ve got a TH400. A rectangular pan with 16 bolts and rounded corners? That’s likely a 700R4/4L60/4L60E series.
This method works like a charm for most GM automatic transmissions, but for manual transmissions or confirming your automatic ID, you’ll need to dig deeper.
Check for RPO Codes
RPO (Regular Production Option) codes provide the most definitive transmission identification for vehicles with their original transmissions. These codes typically begin with “M” and are found on the Service Parts Identification (SPID) label.
Look for these labels in:
- Your glove box
- On the trunk floor
- Inside the driver’s door panel
Common transmission RPO codes include:
- MYC (6L80E)
- M5U (8L90E)
- M5N/M5X (10L90E)
If you have a 2018 or newer GM vehicle, there’s even a QR code on the certification label that contains comprehensive vehicle information including RPO codes when scanned.
Find the ID Tags and Casting Numbers
GM transmissions feature various identification tags and casting numbers that provide detailed information about your specific unit.
Here’s where to look:
- TH350: VIN stamping on driver’s side housing near shifter, right side above pan, or passenger side bellhousing flange
- TH400: VIN stamped on machined surface above pan on driver’s side
- 4L80E: Metal tag riveted to passenger side of transmission
- Modern transmissions: Various electronic control module locations
The casting numbers follow specific formats that can tell you exactly when and where your transmission was made.
Manual Transmission Identification Methods
GM manual transmissions require different identification approaches since they lack transmission pans. The three primary types—Muncie, Saginaw, and Borg-Warner T10—can be distinguished by their construction materials and design features.
Material and Construction Differences
Muncie Transmissions:
- Aluminum case, side cover, and tailshaft housing
- Seven bolts securing side cover
- Reverse shifter arm located on tailshaft housing
- Smooth appearance due to aluminum construction
Saginaw Transmissions:
- Cast iron case and side cover
- Seven bolts on side cover (similar to Muncie)
- Reverse shifter arm on side cover
- First letter of casting number: “S” for 3-speed, “R” for 4-speed
Borg-Warner T10:
- Cast iron case with aluminum side cover and tailshaft
- Nine bolts securing side cover
- Reverse shifter arm on tailshaft housing
- Some models feature aluminum cases with cast iron side covers
Input Shaft Groove System
Manual transmissions often feature grooves cut into input shafts to indicate gear ratios. This is especially useful for identifying specific Muncie and Saginaw transmissions.
Saginaw 4-Speed Groove System:
- No grooves: 2.84/2.01/1.34/1.00 ratios
- 1 groove: 2.54/1.80/1.44/1.00 ratios
- 2 grooves: 3.11/2.20/1.47/1.00 ratios
- 3 grooves: 3.50/2.46/1.65/1.00 ratios
Muncie Groove System:
- M20 (wide ratio): Two grooves on input shaft (1966+)
- M21 (close ratio): One groove on input shaft
- M22 “Rock Crusher”: No grooves on input shaft
The grooves are cut circumferentially around the input shaft and can typically be seen without disassembling the transmission.
Modern Electronic Transmission Identification
If you’re working with a newer GM vehicle, you’re dealing with electronic transmissions that require different identification methods.
6L80E Series (2006-2017)
The 6L80E is a six-speed automatic with electronic control. Look for:
- RPO code MYC for 6L80, MYD for 6L90
- Maximum input torque: 440 ft-lbs
- Distinctive lack of bands, uses clutch-to-clutch shifting
- Large rectangular pan shape with 13-15 bolts
This transmission was commonly paired with LS engines in trucks, SUVs, and performance cars like the Camaro and Corvette.
8L90E Series (2015-present)
The eight-speed automatic 8L90E is found in many late-model GM performance vehicles. Identifying features include:
- RPO codes M5U, M5T for various applications
- Advanced solenoid control with unique current modulation
- Requires specialized programming for component replacement
- Typically found in trucks, SUVs, and high-performance cars
10L90E Series (2018-present)
The ten-speed automatic 10L90E represents the latest GM transmission technology. Look for:
- RPO codes M5N, M5X for different variants
- Co-developed with Ford Motor Company
- Found in high-performance and high-torque applications
- Requires specialized diagnostic equipment for service
For electronic transmissions, a diagnostic scan tool is often the most reliable way to confirm the exact model you’re working with.
Decoding Casting Numbers and Date Codes
GM transmission casting numbers and date codes provide manufacturing information that can help you date and identify your transmission precisely.
Pre-1967 Format:
- Plant prefix code + numerical date + shift code (D/N)
- Example: C531D (Cleveland plant, May 31st, day shift)
Post-1967 Format:
- Transmission type + year + month letter + day
- Example: P9E03 (Powerglide, 1969, May, 3rd day)
Month codes follow this pattern: A=Jan, B=Feb, C=Mar, D=Apr, E=May, H=Jun, K=Jul, M=Aug, P=Sep, R=Oct, S=Nov, T=Dec.
These codes are usually stamped directly onto the transmission case and can help verify the authenticity of rare or desirable transmission models.
VIN Integration for Exact Matching
Many GM transmissions include partial VIN information stamped into the case, linking the transmission to its original vehicle. This is especially useful for collectors or restoration projects.
Partial VIN Format:
- Division ID number
- Model year digit
- Assembly plant letter
- Last six digits of vehicle VIN
For example, a stamp reading “16B123456” would indicate:
- 1 = Chevrolet division
- 6 = 1976 or 1986 model year
- B = Baltimore assembly plant
- 123456 = vehicle serial number
This can help you confirm whether the transmission is original to the vehicle or a replacement.
Electronic Diagnostic Identification
Modern GM transmissions require electronic diagnostic tools for complete identification. The NHTSA’s VIN decoder can provide basic transmission information based on your vehicle’s VIN.
For more detailed analysis, you’ll need:
- GM Tech 2 Scanner (pre-2013 vehicles)
- GM MDI with GDS2 software (2010+ vehicles)
- Professional OBD2 scanners with GM-specific capabilities
These tools can read transmission-specific data, including:
- Exact model identification
- Current programming version
- Solenoid and clutch operation
- Pressure test results
- Shift adaptation data
If you don’t have access to these tools, most auto parts stores offer free diagnostic scanning that can at least confirm the transmission model.
Overcoming Common Identification Challenges
Several factors can complicate GM transmission identification. Here’s how to deal with them:
Age-Related Issues
If you’re working with an older transmission, you might encounter:
- Missing or illegible ID tags
- Painted-over identification numbers
- Corrosion affecting casting numbers
- Aftermarket cases lacking original identification
In these cases, use multiple identification methods. If the pan shape indicates a TH400 but you can’t find the ID tag, check the bolt patterns on the bellhousing, tailhousing dimensions, and shifter configuration to confirm.
Modification Considerations
Modified transmissions present unique challenges:
- Rebuilt transmissions may have different tags
- Performance modifications affecting original specifications
- Swapped transmissions not matching vehicle VIN records
When dealing with modified transmissions, focus on the physical characteristics rather than tags or electronic identifiers. The fundamental design elements like valve body configuration, gear train layout, and case dimensions don’t change even with performance modifications.
GM Transmission Evolution Timeline
Understanding when different transmission models were introduced can help narrow down possibilities, especially for classic vehicles:
| Year Range | Notable Transmissions | Key Characteristics |
|---|---|---|
| 1950-1963 | PowerGlide (early) | Cast iron case, 1 forward gear |
| 1962-1973 | PowerGlide (late) | Aluminum case, 1 forward gear |
| 1969-1986 | TH350/TH350C | 3 speeds, compact design |
| 1964-1990 | TH400/3L80 | 3 speeds, heavy-duty design |
| 1982-1993 | 700R4/4L60 | 4 speeds, hydraulic control |
| 1993-2013 | 4L60E/4L65E/4L70E | 4 speeds, electronic control |
| 1991-2013 | 4L80E/4L85E | 4 speeds, heavy-duty electronic |
| 2006-2017 | 6L80E/6L90E | 6 speeds, fully electronic |
| 2015-present | 8L90E | 8 speeds, advanced electronic |
| 2018-present | 10L90E | 10 speeds, latest technology |
This timeline can help you rule out certain transmissions based on your vehicle’s year of manufacture.
Using Multiple Methods for Certainty
The most reliable approach to GM transmission identification involves cross-checking results from multiple methods. For example:
- First, identify the pan shape and bolt count
- Verify with RPO codes if available
- Check casting numbers and date codes
- Confirm with electronic diagnosis for modern transmissions
By using multiple verification methods, you can overcome the limitations of any single technique and be certain about the transmission you’re working with.
Identifying GM Transmissions Without Removing Them
Sometimes you need to identify a transmission without removing it from the vehicle. Here’s how:
- Crawl under the vehicle with a flashlight to examine the pan shape
- Check for identification tags visible from underneath
- Note the shifter pattern and number of forward gears
- Look up the RPO code in the glove box or door jamb
- Use an OBD scanner to read transmission data (for electronic models)
- Count speedometer cable drive gear teeth if accessible
These steps can give you a good indication of what transmission you’re working with without the hassle of removal.
Differences Between Similar GM Transmissions
Some GM transmissions look very similar but have important differences:
TH350 vs. TH350C
Both have 13-bolt pans with similar shapes, but:
- TH350C has a cooling line running to the front of the transmission
- TH350C has provisions for a lockup torque converter
- TH350C is typically found in later model vehicles (1980s)
700R4 vs. 4L60 vs. 4L60E
All have 16-bolt pans with similar rectangular shapes, but:
- 700R4 (1982-1992): Fully hydraulic control, TV cable
- 4L60 (1993-1994): Updated 700R4 with minor changes, still TV cable
- 4L60E (1995+): Electronic control, no TV cable, electronic connector
6L80E vs. 6L90E
These look nearly identical externally, but:
- 6L90E has stronger internal components
- 6L90E typically paired with higher torque engines
- 6L90E often found in 3/4 and 1-ton trucks
The differences are mainly internal and in the electronic programming, making RPO codes the most reliable way to distinguish between them.
Preparing for a Transmission Swap or Rebuild
Once you’ve identified your GM transmission, you can properly prepare for a swap or rebuild:
- Research common failure points for your specific model
- Determine compatibility with other GM vehicles
- Identify required adapters for engine swaps
- Source the correct rebuild kit or replacement parts
- Understand programming requirements for electronic models
Knowing exactly which transmission you have ensures you’ll order the right parts and follow the correct procedures for your specific model.
Having accurately identified your GM transmission, you’re now equipped to maintain, repair, or upgrade it properly. Whether you’re restoring a classic Chevelle with a Muncie 4-speed or troubleshooting a modern Silverado with a 10L90E, the right identification makes all the difference in getting your project done right.